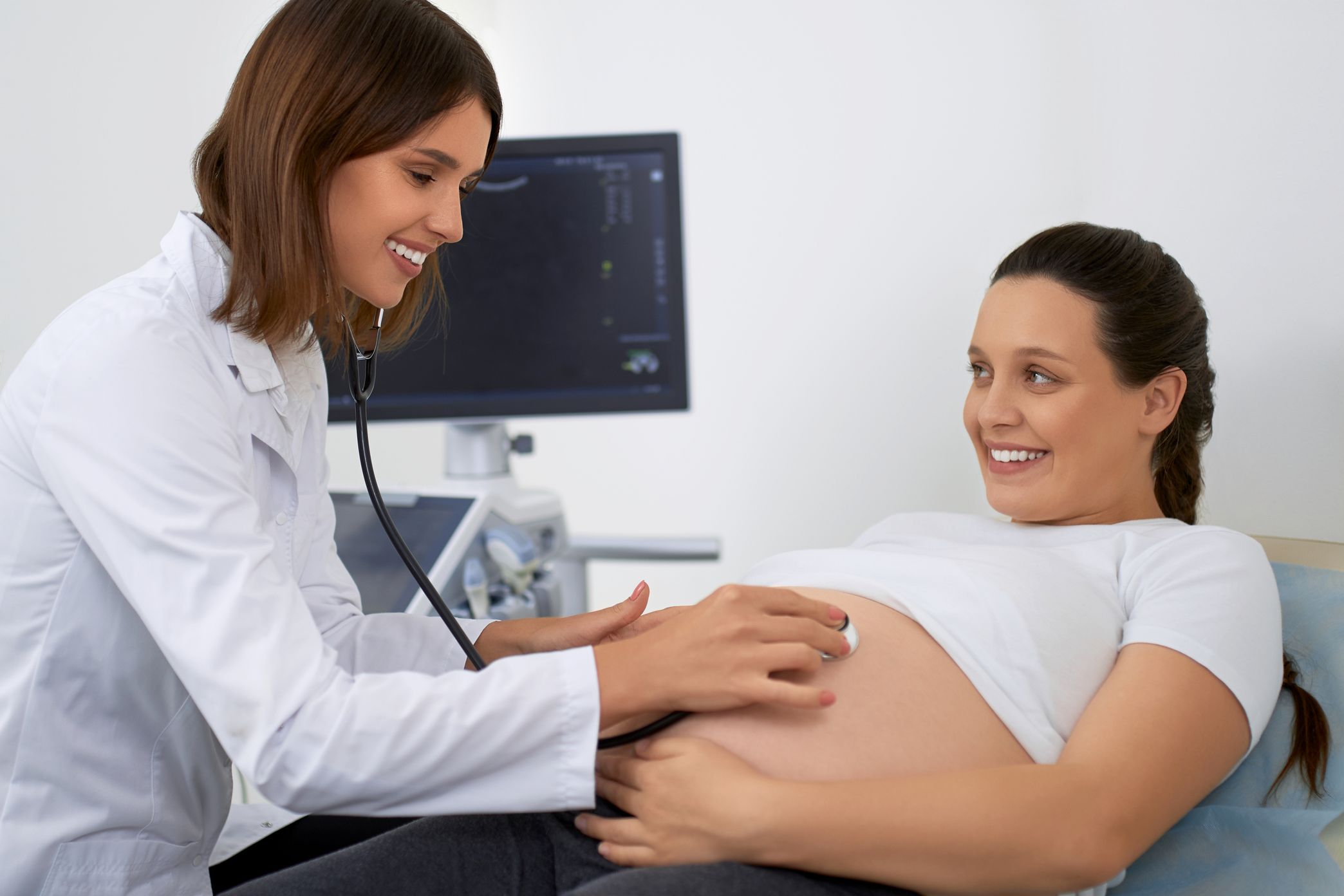
The advent of three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound visualization marks a significant milestone in the evolution of diagnostic imaging, offering a depth of insight previously unattainable with traditional two-dimensional (2D) methods. This innovative technology has substantially improved diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and patient engagement across various medical specialties. This comprehensive article explores the transformative impact of 3D ultrasound visualization, outlining its mechanisms, applications, benefits, and future prospects.
The Advent of 3D Ultrasound Visualization
Three-dimensional ultrasound visualization leverages sound waves and sophisticated computer algorithms to create volumetric images of internal body structures. Unlike 2D ultrasound, which provides flat, linear images, 3D ultrasound compiles multiple slices to form a comprehensive, volumetric representation. This depth-enhanced imagery unlocks a new dimension of diagnostic detail, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize complex anatomical structures with unparalleled clarity.
Mechanism of Action
The 3D ultrasound process begins with the transducer emitting sound waves into the body, which reflect off tissues and return as echoes. Sophisticated software algorithms then reconstruct these echoes into a 3D image that can be rotated, sliced, and scrutinized from multiple angles. This dynamic visualization capability is instrumental in diagnosing conditions, planning treatments, and monitoring therapeutic progress with a degree of accuracy and efficiency that 2D ultrasound cannot match.
Applications Across Medical Specialties
Obstetrics and Gynecology
3D ultrasound has become a cornerstone in obstetrics and gynecology, providing detailed images of the fetus, placenta, and uterus. This technology aids in early detection of fetal abnormalities, enhances the understanding of complex gynecological conditions, and strengthens prenatal bonding by offering expectant parents their first “glimpse” of the unborn child.
Cardiology
In cardiology, 3D ultrasound enables detailed assessments of heart structure and function, offering vital insights into congenital heart defects, valve malfunctions, and myocardial performance. This facilitates more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning for a variety of cardiac conditions.
Oncology
3D ultrasound holds promise in oncology for identifying, characterizing, and monitoring tumors. The ability to precisely delineate tumor volume and morphology aids in biopsy guidance, treatment targeting, and tracking response to therapies.
Surgery
Surgeons utilize 3D ultrasound for preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation, minimizing surgical invasiveness and improving outcomes. This is particularly evident in fields such as neurosurgery and orthopedics, where precise anatomical visualization is crucial.
Benefits of 3D Ultrasound Visualization
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
The depth and detail afforded by 3D ultrasound visualization significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy, reducing the risk of misdiagnosis and ensuring appropriate treatment planning.
Improved Patient Communication and Engagement
The lifelike, intuitive images produced by 3D ultrasound facilitate better patient-provider communication. Patients can visualize and understand their medical conditions more clearly, leading to increased engagement in their care.
Non-Invasive and Cost-Effective
As a non-invasive technique, 3D ultrasound poses minimal risk to patients while offering significant cost advantages over more expensive imaging modalities, such as CT scans and MRIs.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its significant advantages, 3D ultrasound visualization is not without challenges. The quality of images can be influenced by patient factors such as body habitus. Operator skill and experience play critical roles in image acquisition and interpretation.
Future Perspectives
The future of 3D ultrasound visualization is bright, with ongoing advancements in transducer technology, software algorithms, and machine learning poised to further enhance image quality and diagnostic capabilities. The integration of 3D ultrasound with other imaging modalities and telemedicine platforms promises to expand its utility and accessibility, underscoring its role in advancing precision medicine.
Conclusion
Three-dimensional ultrasound visualization represents a paradigm shift in medical imaging, offering a more nuanced and comprehensive view of human anatomy and pathology. Its impact spans from improving diagnostic accuracy and patient care to enhancing medical education and research. As technology continues to evolve, the potential applications and benefits of 3D ultrasound are set to expand, solidifying its role as an indispensable tool in modern medicine’s diagnostic arsenal.