Skills for Enhancing Clinical Decision-Making
Accurate clinical assessments are a cornerstone of effective patient care, ensuring that healthcare providers make informed decisions that lead to better health outcomes. With advancements in medical technologies, the availability of practical tools for assessments has expanded, giving clinicians more resources to evaluate their patients thoroughly and accurately. From physical examinations to sophisticated diagnostic tools, accurate assessments are essential for diagnosing conditions, planning treatments, and monitoring patient progress.
In this article, we will explore some of the most practical tools and techniques used for accurate clinical assessments, their significance in improving patient outcomes, and how healthcare professionals can integrate them into everyday practice.
The Importance of Accurate Clinical Assessments
Before diving into specific tools, it is important to understand why accurate assessments matter. Clinical assessments help clinicians to:
- Identify health issues early: Early detection of diseases can prevent complications, reduce the severity of conditions, and improve patient survival rates.
- Develop appropriate treatment plans: A thorough assessment allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to the specific needs of the patient.
- Monitor progress: Accurate assessments help track the effectiveness of treatments, allowing for adjustments when necessary.
- Improve patient satisfaction: A precise assessment builds patient confidence, as they feel that their health is being addressed comprehensively.
1. Physical Examination Tools
Despite the growing reliance on advanced technology, physical examinations remain a fundamental aspect of clinical assessments. Key tools include:
- Stethoscope: A stethoscope is one of the most basic yet crucial tools in a clinical setting. It allows healthcare professionals to listen to internal sounds such as heartbeats, lung function, and bowel movements. Any abnormal sounds can indicate conditions like arrhythmias, fluid in the lungs, or digestive issues.
- Otoscope: This instrument is used to examine the ear canal and eardrum, helping detect infections, blockages, or injuries in the ear. Early detection of ear conditions can prevent complications like hearing loss.
- Blood Pressure Cuff (Sphygmomanometer): Accurate measurement of blood pressure is crucial in assessing a patient’s cardiovascular health. Hypertension or hypotension can indicate underlying health problems like heart disease or kidney disorders.
- Thermometer: A simple yet essential tool for assessing body temperature. Fever can be an early sign of infections, inflammation, or other systemic issues.
2. Laboratory Testing
Laboratory tests provide objective data that complement physical assessments. Some of the most common and practical lab tests for accurate clinical assessments include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures different components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It helps diagnose conditions like anemia, infections, and blood disorders.
- Blood Chemistry Tests: These tests measure electrolytes, glucose, enzymes, and other important substances in the blood. They help assess organ function (e.g., liver and kidney), electrolyte balance, and metabolic health.
- Urinalysis: This test evaluates the content and composition of urine, aiding in the diagnosis of kidney diseases, infections, and metabolic disorders like diabetes.
- Lipid Panel: A lipid panel measures cholesterol levels, providing important information about cardiovascular health and the risk of heart disease or stroke.
3. Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques have revolutionized clinical assessments, allowing clinicians to see inside the body non-invasively. Some essential imaging tools include:
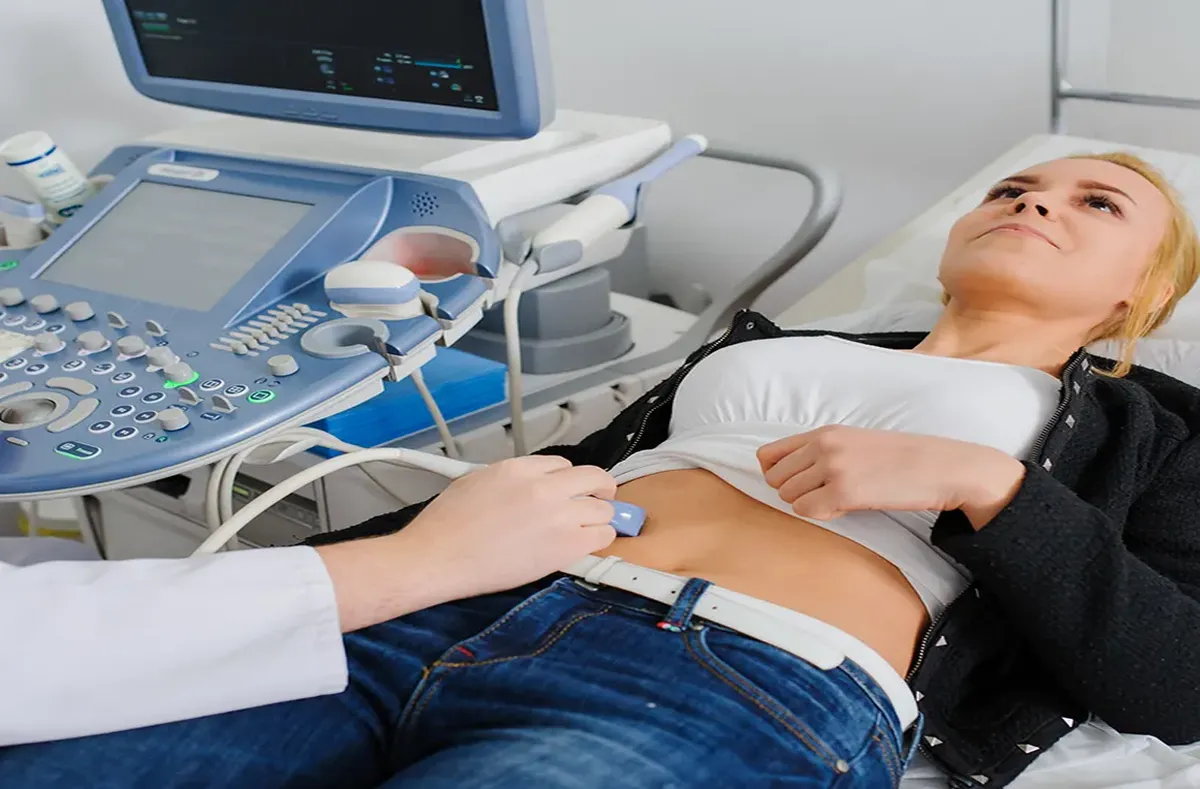
- Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound is a safe and non-invasive tool that uses sound waves to create images of internal organs. It is commonly used in obstetrics, cardiology, and to evaluate soft tissues, the abdomen, and the musculoskeletal system.
- X-rays: X-rays remain one of the most practical and widely used imaging tools for assessing bones, joints, and internal organs. They are particularly useful in diagnosing fractures, infections, and lung conditions.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans provide more detailed images than X-rays, offering cross-sectional views of the body. They are crucial for diagnosing complex conditions like tumors, internal injuries, and vascular diseases.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues. It is particularly useful for assessing the brain, spinal cord, and joints.
4. Digital Tools and Wearable Technology
In recent years, digital tools and wearable devices have become valuable assets in clinical assessments. These technologies offer continuous, real-time monitoring of vital signs and other health metrics, improving the accuracy of assessments.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs provide comprehensive data on a patient’s medical history, treatments, and lab results, streamlining the clinical assessment process by giving healthcare professionals immediate access to essential information.
- Wearable Devices: Devices such as fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, and smartwatches allow continuous monitoring of vital signs like heart rate, physical activity, and sleep patterns. These devices can alert both patients and clinicians to potential issues before they become serious.
- Telemedicine Tools: Telemedicine has expanded the capabilities of clinical assessments, enabling healthcare providers to assess patients remotely using video consultations, digital stethoscopes, and other telehealth tools. Telemedicine can be especially useful for patients in remote areas or those with limited mobility.
5. Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Point-of-care testing (POCT) is a rapidly growing area that provides immediate diagnostic results during patient visits, reducing the need for multiple appointments. Some common POCT tools include:
- Blood Glucose Monitors: These devices allow for quick and easy measurement of blood glucose levels, especially useful for diabetic patients to manage their condition.
- Rapid Antigen Tests: Often used for detecting infectious diseases such as influenza, COVID-19, or strep throat, these tests offer fast results, enabling clinicians to initiate treatment promptly.
- Portable ECG Machines: Portable electrocardiogram (ECG) devices are used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. They can help detect heart conditions such as arrhythmias, ischemia, or heart attacks.
6. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) are digital tools that aid healthcare professionals in making more accurate clinical decisions. These systems use algorithms, patient data, and medical knowledge to provide recommendations for diagnosis, treatment, and management. CDSS tools help reduce human error, improve diagnosis accuracy, and ensure that clinical decisions are based on the most current medical evidence.
7. Checklists and Clinical Guidelines
In addition to high-tech tools, simple tools like checklists and clinical guidelines are essential for ensuring thorough and consistent clinical assessments.
- Checklists: Checklists help healthcare professionals ensure that they are covering all necessary steps during an assessment. For example, surgical safety checklists are used to minimize errors and improve patient outcomes.
- Clinical Guidelines: Guidelines from reputable medical organizations provide evidence-based recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Following these guidelines ensures that assessments and care are standardized and up-to-date.
FAQ
What is the purpose of a stethoscope in clinical assessments? A stethoscope is used to listen to internal body sounds, such as heartbeats and lung function, helping detect conditions like arrhythmias or fluid in the lungs.
How does an otoscope help in patient assessments? An otoscope allows clinicians to examine the ear canal and eardrum for infections, blockages, or injuries.
Why are blood pressure cuffs important for clinical assessments? Blood pressure cuffs measure blood pressure, which is vital for assessing cardiovascular health and detecting hypertension or hypotension.
What are the benefits of laboratory testing in clinical assessments? Laboratory tests provide objective data, such as blood counts and organ function, which complement physical examinations and aid in diagnosis.
What role does ultrasound play in clinical assessments? Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging tool used to visualize internal organs, soft tissues, and the cardiovascular system, aiding in early diagnosis.
How do wearable devices improve clinical assessments? Wearable devices provide continuous monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate and activity levels, offering real-time data for clinicians.
What is the advantage of point-of-care testing (POCT)? POCT provides immediate diagnostic results, allowing for faster decision-making and reducing the need for follow-up appointments.
How do clinical decision support systems (CDSS) enhance accuracy in assessments? CDSS tools use algorithms and patient data to provide recommendations for diagnosis and treatment, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
What is the function of checklists in clinical assessments? Checklists ensure that healthcare professionals follow all necessary steps during an assessment, reducing the risk of errors.
Why are clinical guidelines important in patient care? Clinical guidelines offer evidence-based recommendations, ensuring that patient care is standardized and aligned with current medical knowledge.
Conclusion
Accurate clinical assessments are the foundation of high-quality healthcare, and the tools available today make these assessments more precise and efficient than ever before. From traditional tools like the stethoscope and blood pressure cuff to advanced imaging techniques and digital health technologies, each tool plays a vital role in the clinical assessment process. By combining physical examinations, laboratory tests, imaging, and digital innovations, healthcare providers can ensure that their assessments lead to better, more informed decision-making and improved patient outcomes.