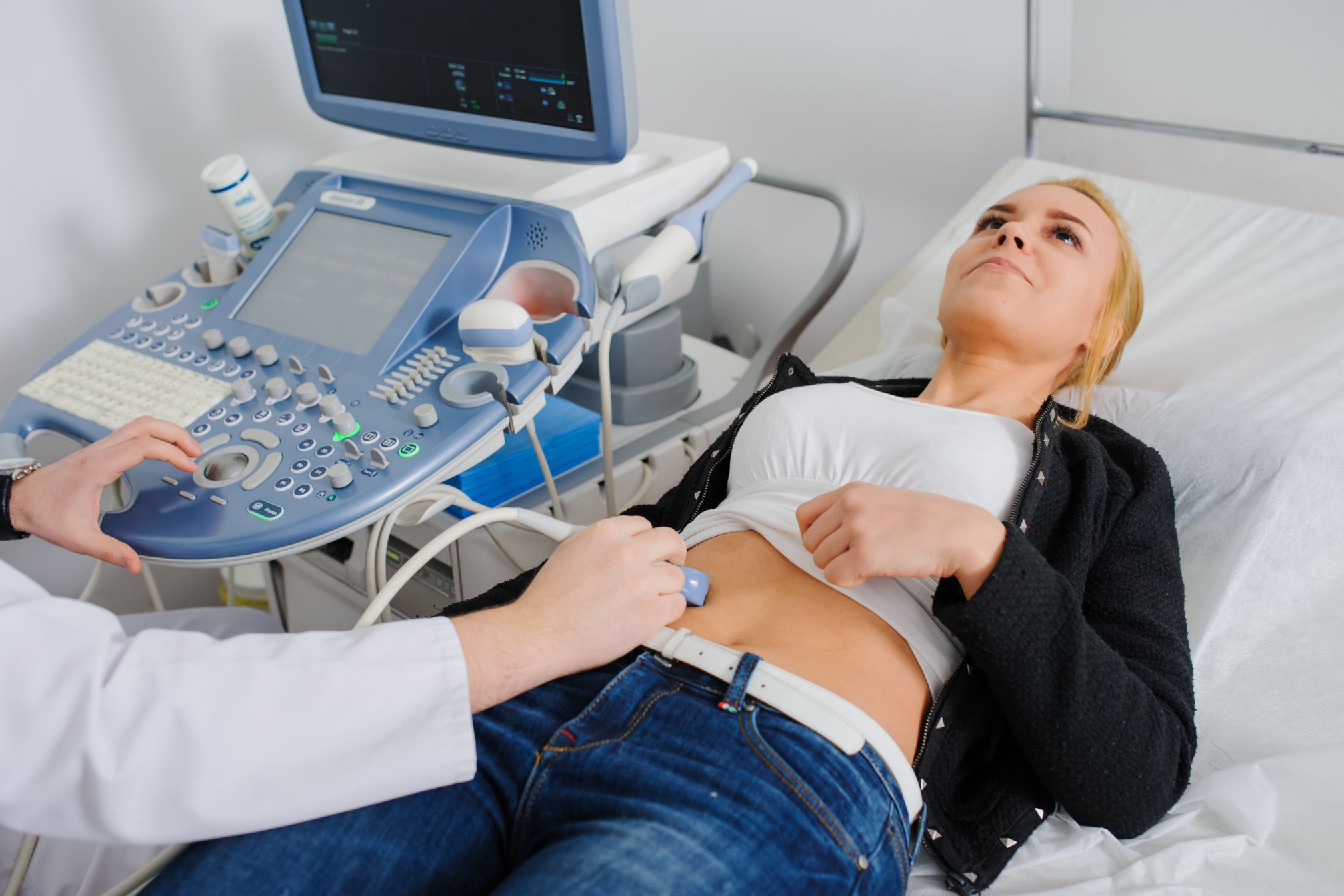
Thoracic ultrasound to the rescue! This phrase might sound dramatic, but when it comes to the real-world application of this incredible technology, it’s no exaggeration. Whether you’re in a high-stakes emergency room or managing chronic conditions in a routine setting, thoracic ultrasound has rapidly become a frontline tool in modern medicine.
Imagine this: A patient arrives at the emergency department, gasping for air, chest tight, and in severe distress. The clock is ticking, and every second counts. Instead of rushing the patient off to radiology for a chest X-ray, the medical team grabs a portable ultrasound machine and gets to work right there at the bedside. Within minutes, the diagnosis is made, and life-saving treatment begins. That’s thoracic ultrasound to the rescue in action.
The Evolution of Thoracic Ultrasound
Thoracic ultrasound might seem like a recent innovation, but its roots stretch back to the early days of ultrasound technology. Originally, ultrasound was used primarily for obstetrics and gynecology, but as technology advanced, so did its applications. Thoracic ultrasound began gaining traction in the 1980s and 1990s, but it wasn’t until the 21st century that it truly became a staple in emergency and critical care settings.
What makes thoracic ultrasound to the rescue such a powerful concept is its ability to provide real-time imaging without the delays and risks associated with traditional imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans. Instead of waiting for radiology reports, clinicians can assess, diagnose, and even begin treating conditions such as pleural effusions, pneumothorax, and pulmonary edema on the spot.
Real-Life Scenarios: Thoracic Ultrasound in Action
Let’s dive into a real-life scenario where thoracic ultrasound to the rescue truly shines.
Case 1: The Silent Pneumothorax
Consider a young man who arrives at the ER after a minor car accident. He’s conscious, alert, and only complains of mild chest pain. A quick physical exam reveals nothing alarming. However, something just doesn’t sit right with the attending physician. Instead of ordering a chest X-ray, they decide to perform a thoracic ultrasound.
Within moments, the ultrasound reveals a small but significant pneumothorax—an air leak in the chest that could have easily been missed. Thanks to thoracic ultrasound to the rescue, the team quickly intervenes, preventing a potentially life-threatening situation.
Case 2: The Hidden Pleural Effusion
Now, picture an elderly woman with a history of congestive heart failure. She’s been feeling more short of breath lately, but her symptoms have been chalked up to her chronic condition. Her doctor, however, suspects something more and opts for a thoracic ultrasound.
The scan reveals a large pleural effusion—fluid accumulating in the space around her lungs. This wasn’t just her heart failure acting up; this was a critical finding that required immediate attention. Once again, thoracic ultrasound to the rescue.
Why Thoracic Ultrasound is a Must-Have in Critical Care
Speed and Accuracy
In medicine, speed often equals survival. Thoracic ultrasound to the rescue isn’t just a catchy phrase; it’s a reality in emergency and critical care. The ability to make quick, accurate diagnoses at the bedside without the need for radiation or complex machinery is a game-changer. For conditions like pneumothorax, where every second counts, thoracic ultrasound is often more sensitive than a chest X-ray, providing a diagnosis when it’s needed most.
Versatility in Application
Thoracic ultrasound isn’t just for emergencies. It’s versatile enough to be used in various settings, from ICU to outpatient clinics. It’s particularly useful in guiding procedures like thoracentesis, where real-time imaging ensures that needles are placed precisely, reducing the risk of complications. In the age of COVID-19, thoracic ultrasound became a lifeline, allowing clinicians to monitor lung involvement without exposing patients to additional risks.
Non-Invasive and Safe
Another reason thoracic ultrasound to the rescue has become a mantra in healthcare is its safety profile. Unlike CT scans or X-rays, thoracic ultrasound doesn’t expose patients to radiation. This makes it an ideal option for repeated use, whether it’s tracking the progress of a condition or guiding a procedure. For pregnant women, children, or anyone where radiation is a concern, thoracic ultrasound offers a worry-free alternative.
The Mechanics Behind Thoracic Ultrasound
You might wonder how this technology works so effectively. At its core, thoracic ultrasound utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create images of the structures within the chest. These sound waves bounce off tissues, and the echoes are captured to form a detailed picture of what’s happening inside the body.
Key Areas of Focus
When we talk about thoracic ultrasound to the rescue, we’re focusing on a few key areas:
- Lungs: Thoracic ultrasound can detect conditions like pneumothorax (air in the chest cavity), pleural effusion (fluid around the lungs), and pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs).
- Pleura: This thin membrane covering the lungs and chest cavity can be easily visualized with ultrasound, allowing for the detection of infections, scarring, or other abnormalities.
- Heart and Diaphragm: While not a replacement for echocardiography, thoracic ultrasound can give quick insights into heart function and diaphragm movement, particularly in emergency settings.
Training and Expertise: The Human Element in Thoracic Ultrasound
Of course, thoracic ultrasound to the rescue wouldn’t be possible without skilled clinicians behind the probe. While the technology itself is powerful, it’s the expertise of the operator that makes the difference. Proper training in thoracic ultrasound techniques is crucial for accurate interpretation and effective use.
The Learning Curve
Learning thoracic ultrasound isn’t as daunting as it may seem. Many healthcare professionals can become proficient with focused training sessions, often just a few days in length. Once trained, these clinicians can perform thoracic ultrasound at the bedside, dramatically improving patient care.
Ongoing Education
Thoracic ultrasound is a rapidly evolving field. As new techniques and technologies emerge, ongoing education is vital. Regular training updates and participation in professional workshops help clinicians stay at the forefront of this life-saving tool.
Future of Thoracic Ultrasound: What’s Next?
The phrase thoracic ultrasound to the rescue is likely to become even more common as technology continues to advance. As ultrasound machines become more compact, affordable, and user-friendly, the barriers to widespread adoption are falling.
Miniaturization and Portability
One of the most exciting developments is the miniaturization of ultrasound technology. Handheld devices that fit in a pocket are becoming a reality, allowing thoracic ultrasound to the rescue scenarios to happen not just in hospitals but in ambulances, remote clinics, and even in the field during disasters.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Another promising area is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with thoracic ultrasound. AI-driven algorithms can assist in interpreting images, reducing the learning curve for new users, and increasing the accuracy of diagnoses. This doesn’t mean AI will replace clinicians—far from it. Instead, AI will act as a powerful tool, enhancing the capabilities of thoracic ultrasound and making it even more reliable.
Expanded Clinical Applications
As research continues, we’re likely to see thoracic ultrasound to the rescue being applied to an even broader range of conditions. For example, there’s growing interest in using ultrasound to assess lung function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or to guide the management of complex respiratory conditions in intensive care.
FAQ
What is the purpose of thoracic ultrasound?
The purpose of thoracic ultrasound is to provide real-time imaging of the lungs, pleura, and surrounding structures, enabling quick and accurate diagnosis of various chest conditions such as pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and pulmonary edema without the need for radiation.
How long does a thoracic ultrasound take?
A thoracic ultrasound typically takes about 15 to 30 minutes. The exact duration depends on the complexity of the examination and the specific areas being assessed, but the procedure is generally quick and efficient.
How do you prepare for a thoracic ultrasound?
Preparation for a thoracic ultrasound is minimal. Patients may need to wear comfortable clothing that allows easy access to the chest area. No special diet or fasting is required, and patients can continue taking their medications as usual.
What non-radiologists need to know for thoracic ultrasound?
Non-radiologists should know that thoracic ultrasound is a highly effective, non-invasive tool for diagnosing chest conditions. It requires basic training in ultrasound techniques and interpretation, but it is safe, portable, and can be performed at the bedside.
What structures can be seen with a thoracic ultrasound?
Thoracic ultrasound allows visualization of the lungs, pleura, diaphragm, and sometimes the heart and chest wall. It can detect abnormalities like fluid collections, air leaks, or lung consolidation, making it a valuable tool in assessing thoracic conditions.
What is a thoracic appointment for?
A thoracic appointment typically involves an assessment of the chest and lungs, often using thoracic ultrasound. The purpose is to diagnose or monitor conditions like pleural effusions, lung infections, or other thoracic abnormalities, guiding appropriate treatment.
What are the 10 signs of a lung ultrasound?
The 10 signs of a lung ultrasound include A-lines, B-lines, lung sliding, consolidation, pleural effusion, pneumothorax, air bronchograms, subpleural nodules, pleural thickening, and diaphragmatic movement. These signs help diagnose various lung conditions.
What does a thoracic scan show?
A thoracic scan shows detailed images of the lungs, pleura, and surrounding chest structures. It can reveal conditions like pleural effusion, pneumothorax, lung consolidation, and other abnormalities, providing critical information for diagnosis and treatment.
What organs are held in the thoracic cavity?
The thoracic cavity houses the lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea, major blood vessels (including the aorta and vena cava), and the diaphragm. These organs play essential roles in respiratory and cardiovascular functions.
Conclusion
Thoracic ultrasound to the rescue isn’t just a slogan; it’s a reality that’s transforming healthcare. From emergency situations to routine monitoring, this technology is proving its worth time and again. It’s fast, accurate, non-invasive, and versatile—everything you could want in a diagnostic tool.
As we look to the future, the role of thoracic ultrasound will only continue to grow. With ongoing advancements in technology and education, thoracic ultrasound to the rescue will be an ever-present force in modern medicine, saving lives and improving outcomes for patients around the world.
So, the next time you hear thoracic ultrasound to the rescue, remember that behind those words lies a powerful story of innovation, expertise, and the relentless pursuit of better healthcare