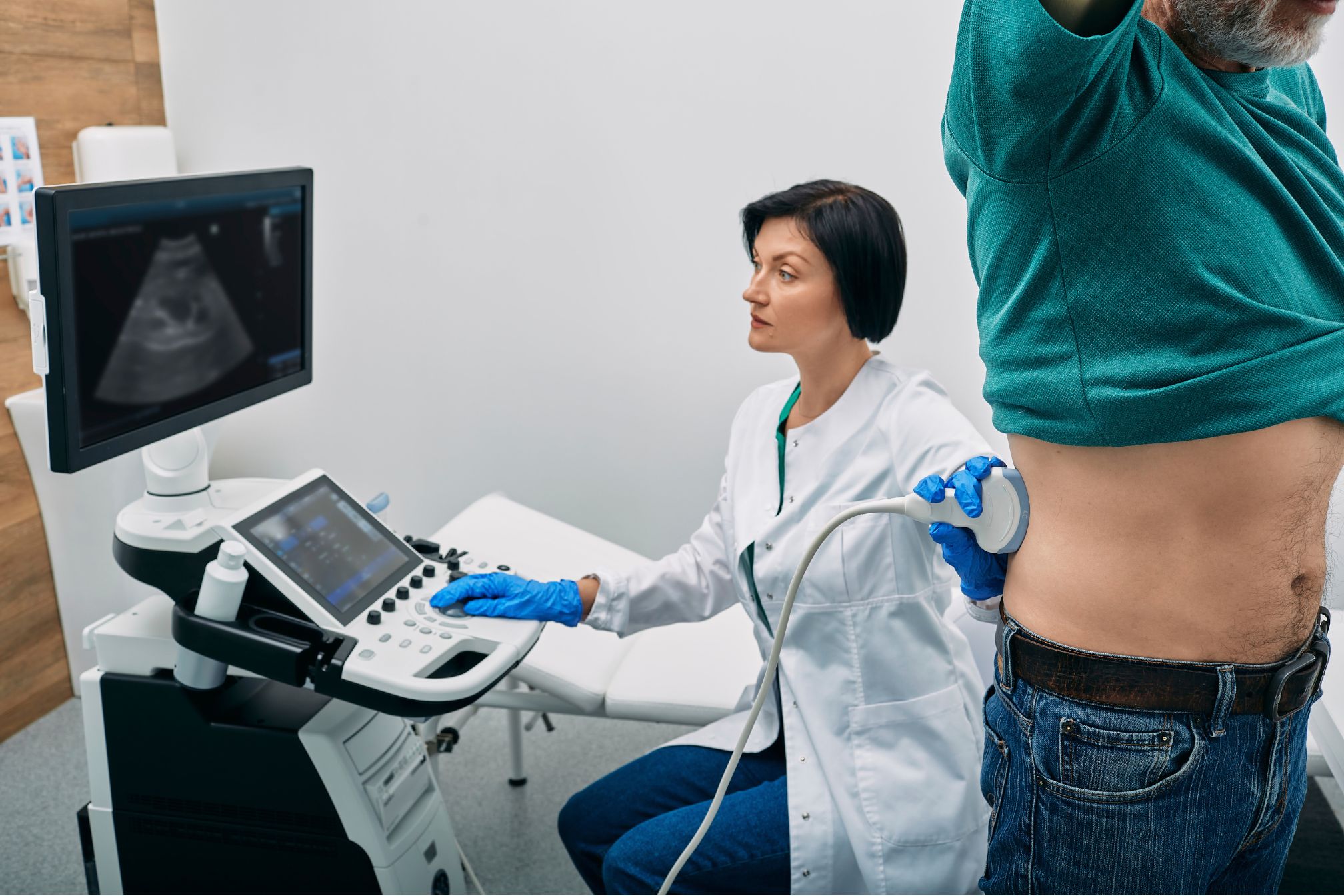
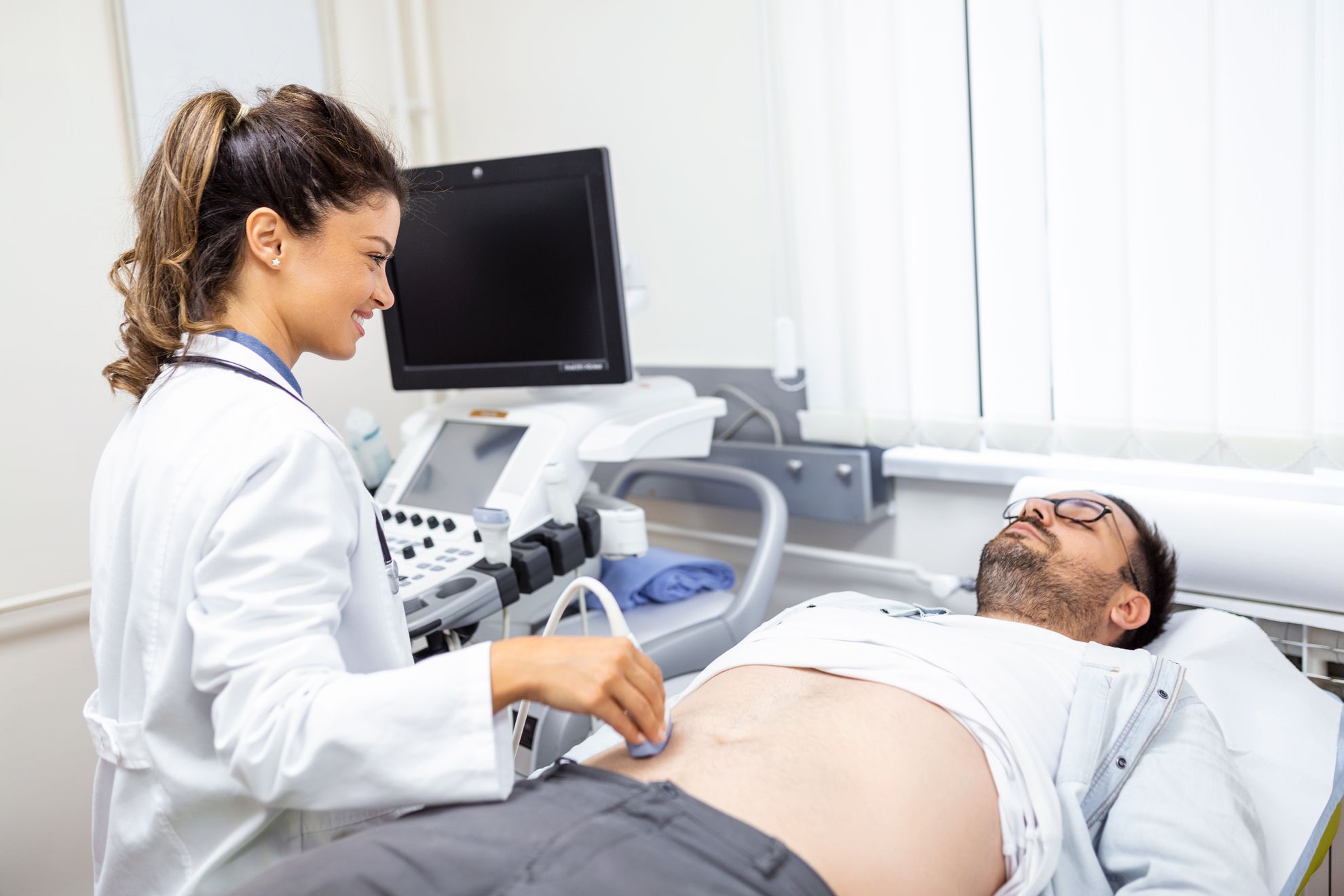
When it comes to medical imaging, transactional Doppler ultrasound plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and assessing various conditions related to blood flow and vascular health. Imagine stepping into a doctor’s office for a routine check-up, and after a few moments, you find yourself looking at a colorful map of your blood vessels on a screen. This captivating technology helps physicians understand how well blood is flowing through your body, offering vital insights into your health.
The Basics of Doppler Ultrasound
So, what exactly is Doppler ultrasound? Let’s break it down. At its core, Doppler ultrasound utilizes sound waves to visualize blood flow. When sound waves hit red blood cells, they bounce back at different frequencies depending on the movement of those cells. This frequency shift, known as the Doppler effect, allows healthcare professionals to determine how quickly and in which direction blood is flowing.
Imagine you’re standing on a sidewalk, and an ambulance speeds past you. As it approaches, the sound of the siren gets louder and higher-pitched; as it moves away, the sound lowers. That’s the Doppler effect in action! In the medical world, this principle helps assess conditions like blood clots, blocked arteries, or other vascular abnormalities.
What Is Transactional Imaging?
Now that we have a grip on Doppler ultrasound, let’s talk about the transactional aspect. Transactional imaging is the conventional ultrasound technique that creates two-dimensional images of organs and structures inside your body. By combining this with the Doppler effect, doctors can visualize not only the structure of blood vessels but also the dynamics of blood flow within them.
Imagine this scenario: You’re at a traffic intersection, watching cars move in different directions. A regular ultrasound gives you a snapshot of the vehicles (the structures), while transactional Doppler ultrasound provides information about their speed and flow patterns—essentially mapping the bustling traffic of your bloodstream.
The Importance of Transactional Doppler Ultrasound
Transactional Doppler ultrasound is crucial for diagnosing various medical conditions. It provides real-time information, enabling doctors to make informed decisions swiftly. Here are some key areas where this technology shines:
Vascular Health
One of the most significant applications of transactional Doppler ultrasound is in assessing vascular health. Conditions like peripheral artery disease (PAD) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can have serious consequences if left untreated. Through this ultrasound technique, physicians can evaluate blood flow in the arteries and veins, identifying blockages or narrowing.
Cardiology
In cardiology, transactional Doppler ultrasound serves as a non-invasive method for examining heart function. For example, it can assess how well the heart valves are working and detect congenital heart defects in children. This technology allows cardiologists to visualize blood flow patterns, giving them a clear picture of cardiac health.
Obstetrics
Expecting mothers often undergo transactional Doppler ultrasound to monitor fetal development and placental blood flow. This not only provides reassurance to parents but also helps healthcare providers ensure that the baby is receiving adequate blood supply. In this way, Doppler ultrasound becomes a bridge between a mother and her unborn child.
Pre-operative Assessments
Before performing certain surgical procedures, doctors may use transactional Doppler ultrasound to evaluate blood flow to specific areas of the body. This information is crucial in planning surgeries, especially for procedures involving the heart, legs, or other vascular structures.
The Procedure: What to Expect
If you’re scheduled for a transactional Doppler ultrasound, you might wonder what the experience will be like. Here’s a walkthrough of the typical procedure:
Preparation
Before your appointment, there’s usually little to no preparation required. You might be advised to wear loose-fitting clothing to facilitate easier access to the area being examined. If you’re having an abdominal ultrasound, you might need to avoid eating for a few hours prior to the procedure.
During the Procedure
Once you arrive, a healthcare professional will guide you to a comfortable examination room. You’ll lie down on an examination table, and the technician will apply a gel to your skin. This gel helps transmit sound waves more effectively.
Next, the technician will use a handheld device called a transducer, moving it over the area of interest. As the sound waves travel through your body, they reflect off red blood cells and return to the transducer. The machine then converts these signals into images and sound patterns that the technician and your doctor will analyze.
Post-Procedure
The entire process typically takes about 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the examination. After the procedure, you can resume your normal activities immediately. The results are usually available within a day or two, and your healthcare provider will discuss the findings with you.
Real-Life Impact of Transactional Doppler Ultrasound
Let’s delve into a real-life scenario to illustrate the significance of transactional Doppler ultrasound.
Imagine a middle-aged man named John who visits his doctor for a routine check-up. He has been feeling some unusual fatigue and leg pain, particularly when he walks. Concerned, his doctor recommends a transactional Doppler ultrasound to assess his vascular health.
During the examination, the technician identifies reduced blood flow in John’s legs, indicating potential peripheral artery disease. This early detection allows the doctor to recommend lifestyle changes and treatments that can significantly improve John’s quality of life.
Without the insights provided by the transactional Doppler ultrasound, John’s condition might have gone unnoticed, leading to more severe health complications down the road.
Advantages of Transactional Doppler Ultrasound
The benefits of transactional Doppler ultrasound extend far beyond just visualization. Here are some key advantages:
Non-Invasive and Safe
Unlike traditional surgical procedures, Doppler ultrasound is non-invasive and poses minimal risks. There are no needles, incisions, or radiation exposure, making it a safe option for patients of all ages, including pregnant women and children.
Real-Time Results
Transactional Doppler ultrasound provides immediate feedback, allowing doctors to assess conditions on the spot. This immediacy is crucial in emergency situations where quick decisions can save lives.
Comprehensive Assessments
By combining anatomical and physiological data, this ultrasound technique offers a comprehensive view of vascular health. Physicians can visualize the structure of blood vessels while also assessing blood flow dynamics, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
Cost-Effective
Compared to other imaging modalities like CT or MRI scans, transactional Doppler ultrasound is relatively cost-effective. This accessibility allows more patients to benefit from vascular assessments without the burden of high expenses.
Limitations of Transactional Doppler Ultrasound
While transactional Doppler ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic tool, it does have some limitations.
Operator Dependent
The accuracy of the results heavily depends on the technician’s skill and experience. Inexperienced operators may miss crucial details, potentially leading to misdiagnoses.
Limited Depth Penetration
In some cases, especially with obese patients, the sound waves may not penetrate deeply enough to visualize blood flow accurately. This limitation can affect the clarity of images and the overall diagnostic capability.
Interpretation Challenges
Interpreting the results of a Doppler ultrasound requires expertise. Physicians must consider various factors, such as patient history and other clinical findings, to arrive at a correct diagnosis.
The Future of Transactional Doppler Ultrasound
As technology advances, the future of transactional Doppler ultrasound looks promising. Innovations in imaging techniques and software may enhance the accuracy and reliability of Doppler assessments. Researchers are continually exploring ways to integrate artificial intelligence (AI) into ultrasound interpretation, potentially revolutionizing the field.
Imagine a world where AI assists healthcare providers in analyzing ultrasound images, reducing human error and speeding up the diagnostic process. With ongoing advancements, the potential for improved patient outcomes is immense.
Conclusion
Transactional Doppler ultrasound is an invaluable tool in modern medicine, offering insights into vascular health that can change lives. From detecting potential health issues to guiding treatment decisions, its applications are vast and impactful. The combination of real-time imaging and blood flow assessment enables healthcare providers to deliver personalized care tailored to individual needs.
So, the next time you find yourself in a doctor’s office, don’t be surprised if you see colorful images of your blood vessels flashing across a screen. That’s the magic of transactional Doppler ultrasound, working behind the scenes to keep you informed about your health