In the dynamic realm of medical imaging, the advent of three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound technology marks a significant leap forward. Moving beyond the traditional two-dimensional (2D) snapshots of the body’s internal structure, 3D ultrasound scanning techniques offer a more comprehensive and nuanced view, revolutionizing diagnostics, patient care, and even the educational journey of medical professionals. This article explores the intricacies of 3D ultrasound scanning techniques, their applications, and the impact they have on the medical field.
The Evolution to Three-Dimensionality
Three-dimensional ultrasound transforms how medical professionals visualize and understand human anatomy and pathophysiology. While 2D ultrasound provides flat, linear images, 3D ultrasound compiles these slices into a volumetric representation, offering a holistic view of the structures being examined.
How It Works
The magic of 3D ultrasound begins with the transducer, which emits sound waves into the body. Unlike in 2D ultrasound, these waves capture a series of slices from different angles within a predefined volume. Advanced computer algorithms then reconstruct these slices into a 3D image that can be viewed, manipulated, and analyzed from any direction, offering unparalleled insights into the body’s internal structures.
Applications and Advantages
Obstetrics and Gynecology
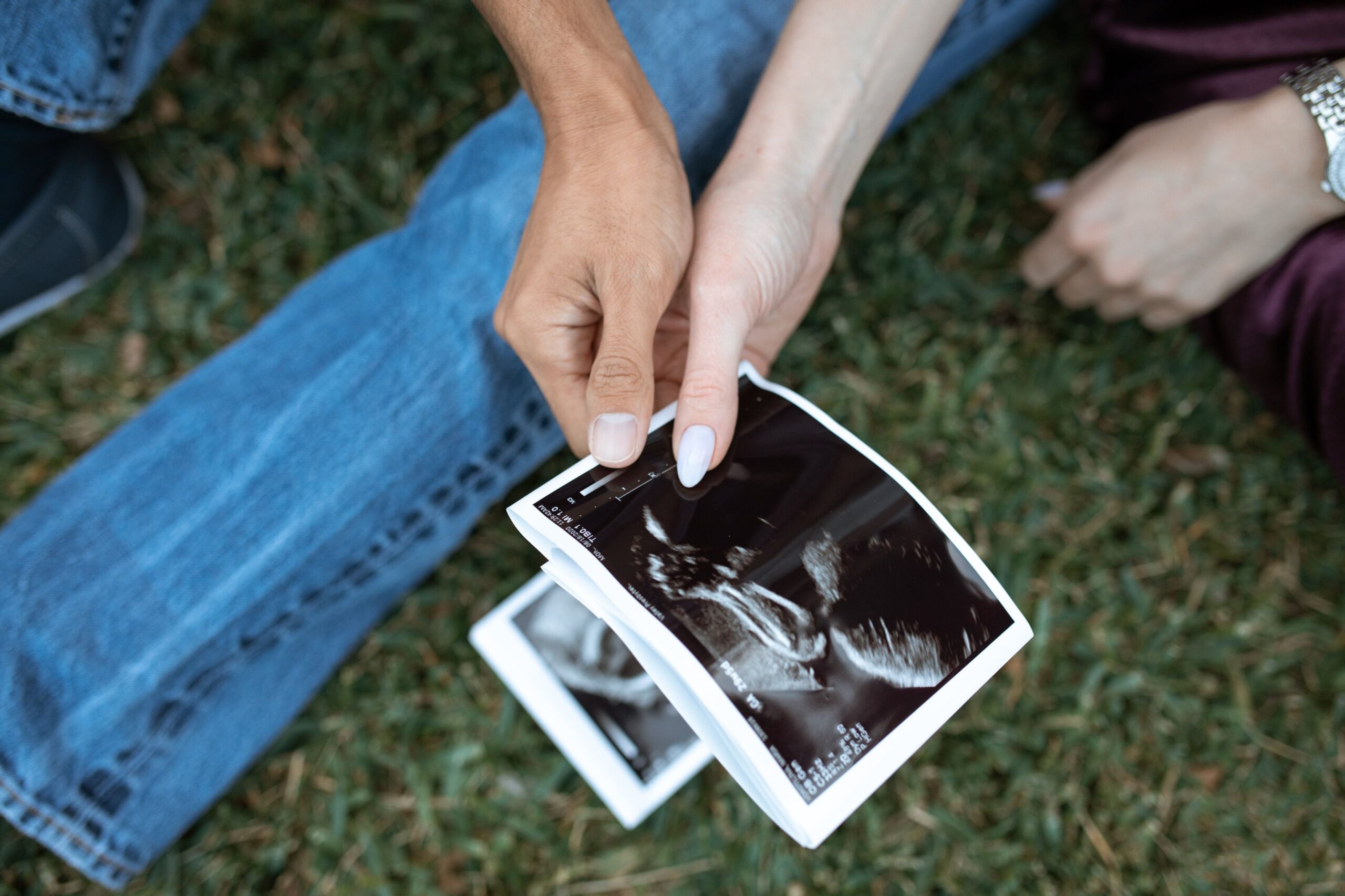
One of the most celebrated applications of 3D ultrasound is in obstetrics and gynecology. It allows for detailed visualization of the fetus in the womb, aiding in the early detection of congenital anomalies, better assessment of fetal growth and development, and fostering a unique emotional bonding experience for expectant parents.
Surgery and Biopsies
3D ultrasound greatly aids surgeons and radiologists in planning and guiding invasive procedures. By visualizing the precise 3D anatomy of interest, professionals can navigate surgical instruments more accurately during biopsies or minimally invasive surgeries, significantly enhancing patient safety and procedural success rates.
Urology and Nephrology
In the realm of urology and nephrology, 3D ultrasound scanning techniques enable detailed examinations of the kidney and bladder, aiding in identifying stones, tumors, and structural anomalies. The volumetric imaging provides a superior perspective, crucial for diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
Research and Education
3D ultrasound has proved to be an invaluable tool in research and education. It offers medical students and researchers a realistic view of human anatomy and physiological processes, enhancing understanding and facilitating innovation in medical techniques and treatments.
Advancements in Image Quality and Functionality
The continuous advancements in 3D ultrasound technology have significantly improved image quality. High-definition rendering techniques now allow for intricate details to be visualized with clarity seldom matched by other non-invasive imaging modalities. Moreover, features such as volume contrast imaging (VCI) enable clinicians to view thin slices of the captured volume, akin to leafing through the pages of a book, providing even deeper insights.
Patient Experience and Engagement
From a patient perspective, 3D ultrasound scanning techniques offer a less intimidating, non-invasive diagnostic approach. The ability to visually comprehend their medical condition through 3D images fosters a better understanding of their health status and treatment options, enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its numerous advantages, the application of 3D ultrasound also faces challenges. The quality of the images can be affected by patient factors such as body habitus and movement. Additionally, the successful acquisition and interpretation of 3D images require considerable operator skill and experience, underscoring the need for specialized training.
Looking Ahead
As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for 3D ultrasound will expand even further. Innovations in software algorithms and transducer technology promise even higher resolution images and faster processing times. The integration of 3D ultrasound with other imaging modalities, such as MRI or CT scans, could pave the way for even more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
Conclusion
Three-dimensional ultrasound scanning techniques represent a paradigm shift in medical imaging, offering a window into the human body with clarity and detail that was once unimaginable. As this technology continues to evolve and become more integrated into various medical specialties, its impact on improving diagnostics, patient care, and medical education is set to grow exponentially. The future of 3D ultrasound holds great promise, heralding new horizons in the quest for advancing human health.